The Signs of Aging
Posted on 22 January 2016 by Ning W
Share this post
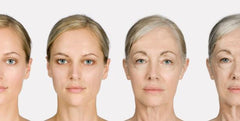
The signs of aging – and how to stop them...... While many of us see wrinkles as an unfortunate part of aging – and are saving our pennies in hopes of having a future face lift – there are in fact a wide range of things that contribute to the aging process. Too much exposure to the sun, sugar consumption and free radicals are all skin enemies, and can show themselves through wrinkles, sagging skin and the loss of your complexion’s vibrant, youthful glow. The passage of time and genetics can also play a role in the aging process, but a little bit of knowledge can go a long way toward preventing wrinkles and bringing the aging process to a halt.
Here Comes the Sun – with Wrinkles
The damaging UV rays of the sun wreak the most havoc and most contribute to the aging process, experts say. That means that if you were a sun worshipper who spent too much time tanning as a teen, it’s likely you’ll eventually see that long-ago damage show itself at some point in your life. Sunscreen, however, can prevent much of the damage, according to a study by Australian researchers released in 2013. Scientists found after a four-year follow-up of more than 900 participants that those who were told to wear sunscreen had fewer signs of aging on the surface of their skin than those who were given no direction regarding sunscreen. “Skin surface patterns reflect the severity of the sun's damage to the deeper skin, especially to the elastic fibers and collagen,” Dr. Adele Green, the study's lead author, told CNN. Sun damage is caused by two different types of radiation – UV-A and UV-B rays. UV-A rays are the ones that are associated with signs of aging, also known as photo-aging, according to Dr. Lawrence Gibson, a professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic. Photo-aging inhibits the skin’s ability to hold its shape, which results in wrinkles. Wearing sunscreen – especially a lightweight version that won’t clog pores – can protect your face and help reduce future signs of aging.
Sugar’s Just Not So Sweet
Because it is found in a wide range of foods including items we wouldn’t suspect such as crackers and bread, it’s hard to avoid sugar. Many of us jump-start our day by stirring a teaspoon of sugar into our morning cup of coffee, never thinking that when it comes to our skin, sugar is just not that sweet. When we consume sugar, it is almost immediately transformed into blood glucose, which our body converts into energy. When levels of blood glucose are high, however – such as those days we pair our coffee with a cinnamon roll - sugar molecules can’t all be used for energy, and the tag-alongs attach themselves to protein molecules. These new sugar proteins are called advanced glycation end products, appropriately known as AGEs. The more sugar we eat, the more AGEs develop. Unfortunately for skin, the proteins sugar finds most appealing are collagen and elastin, which are tasked with keeping skin firm and elastic. AGEs not only damage collagen and elastin when the sugar attaches, they also impact the cells that produce antioxidants, making the essential skin proteins more vulnerable to free radicals. “Number one, the glucose makes the cells abnormal, and number two, it creates free radicals. So you get a double whammy when it comes to aging,” Dr. Cheryl Karcher, a New York City-based dermatologist, said in an interview with Elle magazine. While some glycation is normal – any carb is turned to blood glucose for energy – cutting back on the refined white stuff can have a powerful impact on skin health.
Devastating Free Radicals
Like AGEs, free radicals are damaged cells. They cause damage to the skin because they ravage the body in search of a specific molecule to restore their health, and grab it from whatever cell they run across first. The free radicals heal themselves, but damage or kill the cell from which it stole the needed molecule. Antioxidants – manufactured by the body and found in abundance in brightly-colored fruits and veggies - fight free radicals by donating that necessary molecule without damage to themselves, essentially soothing the savage beast. To make sure you have enough antioxidants on hand to help fight free radicals, which are found in pollution, cigarette smoke and other toxins, its best to fight them from the inside out as well as the outside in. Eat a diet rich in nutrient-dense fruits and vegetables, making sure to take in plenty of skin-friendly Omega 3s, which are found in fish oil, and when you’re searching for a moisturizer, use one that includes antioxidants such as vitamins E, C and A, all of which target the free radicals that do the most damage to skin cells.
Best Creams to Reduce Wrinkles
While it might seem that skin creams that promise to reduce wrinkles are faced with a Herculean task – leaving you questioning if they really work - in truth, the right ingredients, most importantly those that help restore collagen and elastin proteins so skin becomes more elastic, can give you real results – even if you spent your summers sunning on the beach without giving a single thought to wrinkles. The best wrinkle creams use natural ingredients rather than harsh synthetic chemicals that can irritate the sensitive skin of the face. Senvie’s Lift & Firm Deep Anti-Aging Moisturizer has peptides that help encourage the production of collagen and elastin along with natural moisturizers and antioxidants to protect skin from future damage. The formula includes: Matrixyl 3000: This innovative ingredient features two peptides - palmitoyl-tripeptide and palmitoyl-oligopeptide – that work in synergy to encourage the production of collagen and elastin, restoring skin’s radiance and rebuilding strength. Shea butter: This natural nut butter features the same oils produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands, and it melts at skin temperature, absorbing quickly. Shea butter is also packed with vitamin A, an essential antioxidant for skin health. Topheryl acetate: This form of vitamin E addresses signs of aging two ways, first with antioxidants that fight the free radicals that target skin cells, and secondly with rich, healing hydration that improves the look and feel of skin. Glycerin: An emollient that boosts skin’s moisture, glycerin also increases skin’s strength so it is better able to hold its shape, and according to studies helps fight the signs of photo-aging, so skin looks younger, no matter how much time you spent in the sun.



0 comments